What is exFat?
exFAT was primarily developed to replace FAT32 on flash disks to remove the limitations of FAT / FAT32 in terms of single file size (max. approx. 4GB per file) and maximum partition size while maintaining compatibility with many different host devices.
Advantages of exFat: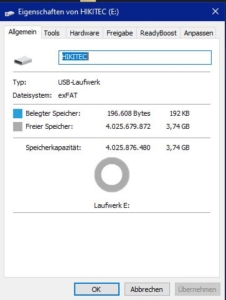
![]() Almost all operating systems can access it
Almost all operating systems can access it
![]() no file size limitations
no file size limitations
Disadvantages of exFat:
![]() slightly slower than NTFS
slightly slower than NTFS
What is NTFS?
Compared to the FAT file system, NTFS offers, among other things, targeted access protection at the file level and greater data security through journaling. However, compatibility is not as broad as with FAT. Another advantage of NTFS is that the file size is not limited to about 4 GB as with FAT16/32.
Advantages of NTFS: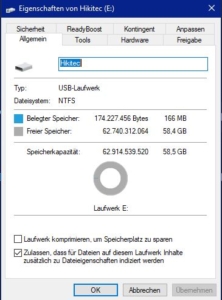
![]() new operating systems can be installed on it
new operating systems can be installed on it
![]() Higher data rates
Higher data rates
![]() File sizes up to 16 TB possible
File sizes up to 16 TB possible
![]() Partition sizes up to 256 TB
Partition sizes up to 256 TB
![]() Writes files “intelligently” to avoid fragmentation
Writes files “intelligently” to avoid fragmentation
![]() logs file changes in case of crashes to avoid data loss
logs file changes in case of crashes to avoid data loss
![]() Files can be encrypted
Files can be encrypted
![]() Compress files and disks possible
Compress files and disks possible
![]() faster defragmentation
faster defragmentation
![]() File accesses can be monitored
File accesses can be monitored
![]() Users can be assigned memory quotas
Users can be assigned memory quotas
Disadvantages of NTFS:
![]() full support only under Windows operating systems
full support only under Windows operating systems
![]() not readable by many devices
not readable by many devices
What are the main file systems in Windows?
- File system
- FAT32
- exFAT
- NTFS 1.0, 1.1, 2
- NTFS 3.0, 3.1, TxF
- max. Partition
- 8 TB
- >8 TB
- >8 TB
- >8 TB
- Usage
- Windows 95b, Windows 98, Windows ME
- Windows CE, Flash memory media
- Windows NT 3.1 bis Windows NT 4.0
- Windows 2000, Windowx XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7
How do I format a USB stick under Windows:
![]() Connect the USB stick to your PC/laptop by plugging it into a free USB port.
Connect the USB stick to your PC/laptop by plugging it into a free USB port.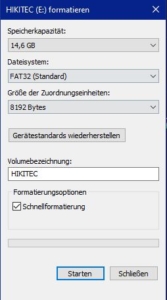
![]() Click the Windows Start icon in the lower left corner and then click “Computer”. Here you can see the connected removable disk.
Click the Windows Start icon in the lower left corner and then click “Computer”. Here you can see the connected removable disk.
![]() Right-click on the USB stick and select “Format …” with the left mouse button. A new window opens.
Right-click on the USB stick and select “Format …” with the left mouse button. A new window opens.
![]() Here you can select the desired file system. If you would like to use your USB stick also in connection with other operating systems, we recommend the default setting “NTFS”.
Here you can select the desired file system. If you would like to use your USB stick also in connection with other operating systems, we recommend the default setting “NTFS”.
![]() If you only want to pair your stick with Windows systems anyway, you can select the “FAT32” setting. However, this file system is only applicable to USB sticks with up to 32 GBytes.
If you only want to pair your stick with Windows systems anyway, you can select the “FAT32” setting. However, this file system is only applicable to USB sticks with up to 32 GBytes.
![]() To format a disk larger than 32 GByte with FAT32, you need an additional program, such as FAT32Formatter.
To format a disk larger than 32 GByte with FAT32, you need an additional program, such as FAT32Formatter.
![]() You can leave the “Storage capacity” and the “Allocation unit size” unchanged.
You can leave the “Storage capacity” and the “Allocation unit size” unchanged.
![]() Behind “Volume label” you can define a name for the USB stick. You can still change this at any time after formatting.
Behind “Volume label” you can define a name for the USB stick. You can still change this at any time after formatting.
![]() As a rule, you can leave or set the checkmark in front of “Quick formatting”, since this type of formatting is completely sufficient in most cases. However, if you want to be on the safe side when deleting data, you can uncheck the box.
As a rule, you can leave or set the checkmark in front of “Quick formatting”, since this type of formatting is completely sufficient in most cases. However, if you want to be on the safe side when deleting data, you can uncheck the box.
![]() Click on “Start” and confirm the security prompt. Afterwards your USB stick will be formatted.
Click on “Start” and confirm the security prompt. Afterwards your USB stick will be formatted.
How do I format a USB stick under CDM*:
![]() Connect the USB stick to your PC by plugging it into a free USB port.
Connect the USB stick to your PC by plugging it into a free USB port.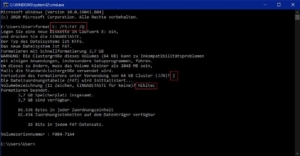
![]() Press the WINDOWS key + R
Press the WINDOWS key + R
![]() Type “CMD” and press Enter. A new black window (console) opens.
Type “CMD” and press Enter. A new black window (console) opens.
![]() Here you have to enter “format”, then the drive letter here in the example “E:” then “/FS” for formatting and then the format here in the example “FAT32”. Confirm your entry with Enter. “format E: /FS:FAT32” ) Here you can get more information: https://ss64.com/nt/format.html
Here you have to enter “format”, then the drive letter here in the example “E:” then “/FS” for formatting and then the format here in the example “FAT32”. Confirm your entry with Enter. “format E: /FS:FAT32” ) Here you can get more information: https://ss64.com/nt/format.html
![]() Now you get again an overview of the USB stick here in the example ” The TYPE of the file system”, the memory size and which formatting was selected. If everything is correct confirm this by pressing J + Enter.
Now you get again an overview of the USB stick here in the example ” The TYPE of the file system”, the memory size and which formatting was selected. If everything is correct confirm this by pressing J + Enter.
![]() Then you can give the USB stick a drive name (11 characters) and confirm with Enter.
Then you can give the USB stick a drive name (11 characters) and confirm with Enter.
![]() Afterwards your USB stick will be formatted.
Afterwards your USB stick will be formatted.
*Use at your own risk! If used incorrectly, you may unintentionally delete important data








